Planning for Windows 7
Phase I: Preparing for Windows 7
Preparing for Windows 7 requires following the process outlined below.
Understanding Windows 7
Users are becoming increasingly computer savvy, and they expect more from the technology they use at work. They expect to be able to work from home, from branch offices, and on the road, without a decrease in productivity. As the needs of users have changed, the demands on IT professionals have increased. Today, IT pros are being asked to provide more capabilities and support greater flexibility, while continuing to minimize cost and security risks. With Windows 7, IT pros can meet the diverse needs of their users in a way that is more manageable. Businesses can enable employees to work more productively at their desks, at home, on the road, or in a branch office. Security and control are enhanced, reducing the risk associated with data on lost computers or external hard drives. Desktop management is streamlined, so it takes less work to deploy Windows 7 and keep it running smoothly. Because Windows 7 is based on the Windows Vista® foundation, companies that have already deployed Windows Vista will find that Windows 7 is highly compatible with existing hardware, software, and tools.
Understanding Windows 7 Features Requirements
A comprehensive list of Windows 7 features are available at . Specific Windows 7 features mentioned below will require detailed planning and assessment before they can be rolled out in an enterprise.
· AppLocker |
· Biometrics |
· Certificates |
· Deployment Tools |
· Group Policy |
· Smart Cards |
· User Account Control |
· Virtual Hard Disks |
· Windows PowerShell |
· Windows Security Auditing |
· Network Enhancements |
· Security Enhancements |
· Enterprise Search |
· Power Management |
· BitLocker |
· BranchCache |
· DirectAccess |
· Remote Access with VPN Reconnect |
· Networking Enhancements |
· Windows XP Mode |
|
Infrastructure Remediation
In order to support the features mentioned above, number of infrastructure components will have to be updated, added and / or enhanced to support Windows 7. Detailed requirements and prerequisites for each of these features are available at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd349336(WS.10).aspx and should be examined in detail.
Phase II: Windows 7 Deployment
Windows 7 deployment means moving from Windows XP and Windows Vista to Windows 7. This can be broadly divided into following phases.
Infrastructure Identification
This phase helps identify current hardware and software deployed in enterprise through
automated collection of information. If a system management tool such as Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager is deployed, use it to obtain appropriate inventories. If no system management tool is in place, the enterprise may decide to put one in place in support of this process. If there is no system management tool in place, the following options exist:
· Scripts
· Manual process
· Dedicated inventory tool
· Application Compatibility Toolkit
· Windows Upgrade Advisor
· Microsoft Software Inventory Analyzer
After the queries are generated and the reports are available, verify that all systems have been included in the report. If systems are missing because the automation tool cannot reach them or because they are in isolated or remote environments, ensure that this additional information is collected before producing the final inventory.
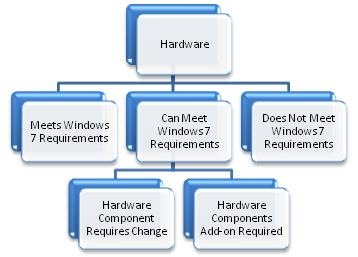
Hardware Remediation
Hardware remediation falls into the following categories.
Based on the above details, hardware remediation plan needs to be created for each of the cases where Windows 7 hardware requirements are not met.
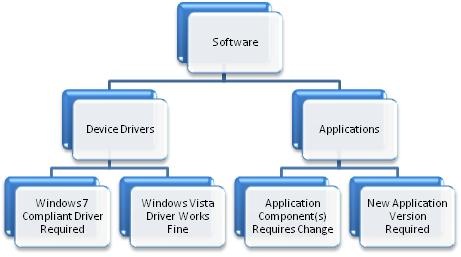
Software (Application) Compatibility
Application compatibility falls into the following categories.
Based on the above details, application remediation plan needs to be created for each of the cases where Windows 7 software (driver and application) requirements are not met. More details available in Application Management section of Business Desktop Deployment Guide (https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc159620.aspx).
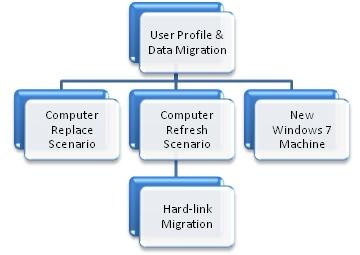
User Profile and Data Migration
User profile and data migration can be performed using number of tools and techniques. Users can be advised to backup their critical data on their own, or, using automated tools data can be backed up on their behalf. User profile and data migration falls into the following categories:
Data backup and restore for all the above scenarios can be achieved using User State Migration Tool (USMT) 4.0. Please review in detail USMT Documentation available at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd560801(WS.10).aspx.
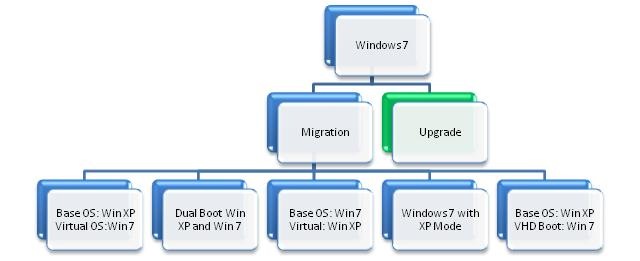
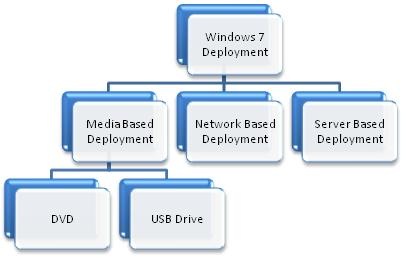
Windows 7 Deployment
There are two options for Windows 7 deployment: Migration and Upgrade. The various options available are shown below:
Once the appropriate option is chosen, the following deployment methods can be used.
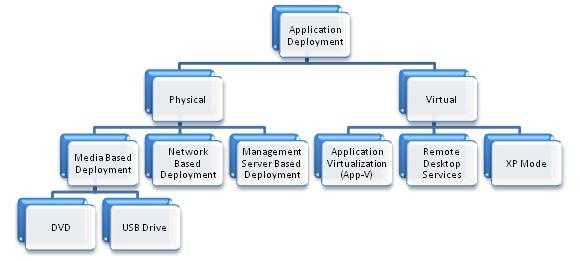
Application Deployment
The options for application deployment are provided below:
Phase III: Managing Windows 7
Windows 7 introduces a number of manageability improvements that can reduce total cost of ownership by helping to increase automation, improve user productivity, and provide flexible administrative control to meet compliance requirements.
Windows 7’s comprehensive scripting abilities, Windows PowerShell™ 2.0 and Group Policy scripting, enhance the productivity of IT professionals by automating those tasks, which reduces errors while improving administrative efficiency.
Windows 7 includes several features that improve user productivity and reduce costs: Built-in Windows Troubleshooting Packs, Improved System Restore tool, Problem Steps Recorder, Improved Resource Monitor and Reliability Monitor.
For IT departments to address their ever-increasing security needs and meet compliance requirements, Windows 7 also supports the following features: AppLocker, BitLocker To Go, DirectAccess.
Altogether, the improvements introduced by Windows 7 can reduce the time IT professionals spend maintaining and troubleshooting, improve user productivity, and enable IT departments to better meet compliance requirements.